Cancer of the Hypopharynx: Early Symptoms, Treated, Metastasis and Detect Cancer
What is cancer of the hypopharynx?
Cancers of the hypopharynx are tumors of the lower pharynx. They are found mostly in males from the ages of 49 to 60.Hypopharyngeal carcinoma may be a malignant neoplasm within the area of the hypopharynx (lower pharynx). Hypopharyngeal carcinoma may be a sort of laryngeal carcinoma.Alcohol abuse and nicotine abuse especially together favor the event of hypopharyngeal cancer. Furthermore, occupational exposure to metal dusts, coal and tar products, and asbestos cement are often carcinogenic. Poor oral hygiene, which results in a pathological composition of saliva, may be a risk factor.
Hypopharyngeal carcinomas are usually moderately differentiated epithelial cell carcinomas. Piriform sinus carcinomas often have a submucosal spread pattern and show only the "tip of the iceberg" in .
There are three clinical regions of the hypopharynx:
Piriform sinus (approx. 90%)Posterior throat wall (approx. 5%)
Post-cricoid region (approx. 5%)
What are the early symptoms of cancer of the hypopharynx?
The symptoms include difficulty in swallowing, lumps in the neck, difficulty in breathing, earaches, cough, and bad breath.Hypopharyngeal carcinoma results in mild dysphagia and aspiration. Furthermore, foreign body sensation, feeling of the world , also as stinging pain, often drawn to the ear, may occur when swallowing. If the carcinoma has spread to the arytenoid , hoarseness and dyspnea also occur. Hypersalivation also can occur. Possibly. bloody sputum occurs in advanced stages.
Since the metastasis occurs very early, the primary symptom is usually an enlargement of the lymph nodes behind and under the ear and at the angle of the jaw, which is typically one-sided and painless.
Direct laryngoscopy shows the tumor mass within the area of the dorsal wall of the hypopharynx. In advanced stages, the tumor has spread to the larynx, prevertebral fascia, and thyroid. Esophagoscopy should rather be performed with a rigid esophagoscope, since the piriform sinus and post-cricoid region can't be seen with a versatile endoscope. Biopsies are taken from different regions of the tumor.
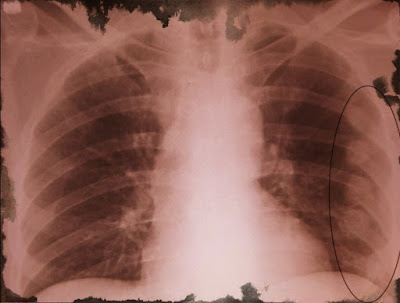
Sonography, CT and / or MRI (of the neck, abdomen and thorax) are often wont to assess the tumor extent within the larynx and neck area, also as metastases more reliably. X-ray chest, PET and bone scintigraphy are helpful for the look for distant metastases.
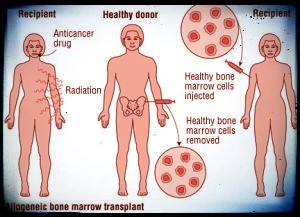
A sole, organ-preserving partial resection of the hypopharynx is performed within the T1 stage and within the T2 stage, NO / N +. within the case of in depth tumors, partial hypopharyngeal resection is performed together with a laryngectomy, a neck dissection and an adjuvant radiation.
As an alternate to surgery , chemotherapy with a platinum-containing chemotherapeutic agent (e.g. cisplatin, carboplatin), also as 5-fluorouracil, bleomycin, mitomycin and methotrexate as polychemotherapy is employed , often together with radiation (radiochemotherapy) or adjuvant with a palliative objective.
In the event of inoperability, an effort is formed to scale back the dimensions of the tumor using the CO2 laser, simultaneous chemoradiation therapy or radiation alone.
End-stage gastrostomy and tracheotomy are often required.
The 5-year survival rate for T1 / T2 tumors is around 30%, for T3 tumors it's only 20%.



Comments
Post a Comment