Where does Melanoma most often metastasize?
What is malignant melanoma?
Malignant melanoma is a less common form of skin cancer. When diagnosed early, it is easily cured. But if it is not found soon enough, it can be very difficult to treat. It is dangerous because, unlike the other skin cancers, it mestastasizes early and spreads quickly. It is one of the more uncontrollable cancers. The cell involved is the melanocyte, the cell which produces melanin, the dark protective pigment of the skin.What is the difference between an ordinary mole and melanoma?
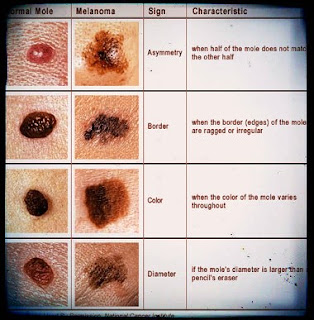
An ordinary mole is evenly colored, and either brown, tan or black. It may be flat or raised. It is round or oval and its edges are sharply defined. An ordinary mole is usually less than 6 millimeters in diameter about the size of a pencil eraser. Ordinary moles may be present at birth. Sometimes several appear at the same time, usually on areas of the skin which have been exposed to the sun. Once the mole develops, it usually stays the same size, shape and color for many years. In older people, moles eventually fade away. The moles that are melanoma, called unusual moles or dysplastic nevi, are more complicated. One half usually does not match the other half that is, they are not round or oval. The color is not uniform. Shades of tan, brown and black, red and pink can be found within the same mole. The edges are ragged, notched or blurred, not clear and sharp. They are usually bigger than a pencil eraser. They usually appear on the back, although they may also be seen below the waist and on the scalp, breast and buttocks.Are new techniques being used to detect melanoma?
There are some new techniques being used. One is an imaging technique called tomographic gallium scanning, which can be used to detect melanoma early. Another approach is the use of antibodies tagged with isotopes to locate the melanoma.Melanoma - Overview (signs and symptoms, pathology, risk factors, treatment)
Should moles which do not show any change be removed ?
No. Moles are very common in various places on the body. It is estimated that most people have from fifteen to fifty of them on the body. Since melanoma is relatively rare about one to two percent of all human cancers the odds that any one mole will become malignant melanoma are less than one in several million. It would be impractical to recommend removal of all moles.Are there any places on the body where moles should be removed?
Moles on the palms of the hands, the soles of the feet, or the genitalia are more apt to turn into malignant melanoma than are moles elsewhere. In addition, if you have a mole in a location that is likely to be repeatedly irritated, such as where a brassiere strap rubs, or where it might be nicked in shaving, it is wise to have it removed. You can have this done in a doctor's office or in an outpatient clinic in the hospital. Usually it will be examined under the microscope just to make certain it is not cancerous.Understanding the Prognosis of Metastatic Melanoma
I am pregnant. The moles on my body are getting darker. Should I be worried about that?
No. Moles on a woman's body may become darker than usual during pregnancy. This is normal and not a sign of melanoma, but you should mention it to your obstetrician.Is it true that a hair growing from a mole means that the mole is not malignant?
Most doctors agree that the presence of hair suggests that a mole is not malignant, but this is not a hard and fast rule. As with any other mole, any change in the color, size, or shape should be regarded as a symptom that should be investigated by the doctor.Who usually gets melanoma?
Most often, malignant melanoma of the skin occurs in people with light complexions, sandy hair, with skins that burn and freckle easily. It is most commonly seen in younger people between 15 and 50 and is about evenly distributed between men and women. Persons with a family history of melanoma or those who have many moles or certain types of moles (dysplastic nevi) are at higher risk. It is now also believed that people who get blistering sunburns early in life are at more than average risk. Although rare in black persons, they can develop this cancer especially on the palms of the hand, the soles of the feet and under the nails. In whites, melanoma is usually found on the trunk area in men, on the lower legs in women. Other common sites are head, neck, and arms.Is melanoma inherited?
There seems to be a predisposition of melanoma in some families. Studies have shown that dysplastic nevi carry with them a very high risk among persons with a family history of melanoma. Suspicious moles should be surgically removed as soon as possible.Persons without a family history of melanoma may also get dysplastic nevi. The risk of melanoma is increased for these people but it is not as high as for those with a family history of the disease. Their moles should be watched carefully for any changes and removed if changes take place.
Are there any prevention guidelines for a person at high risk of developing melanoma?
People who are at high risk for developing melanoma should follow these guidelines:• Do a monthly skin exam. Get familiar with your skin and the pattern of moles, freckles and beauty marks on it.
• If you see any changes in your skin, see the doctor right away.
• Find a doctor with experience in melanoma for your skin care. This doctor should know the importance of your family background and be willing to remove any changing skin lesions early.
• Spend as little time in the sun as you can. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the major known factor for causing melanoma. Avoid getting sunburned, and do not try to get a "good" tan. Use a 15 SPF-rated sunscreen,especially from 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. Reapply the sunscreen after swimming or sweating. Remember that UV radiation can pass through clouds or be reflected from snow or water. Thus, sunscreens may be needed even on a cloudy or winter day.
• Avoid indoor sunlamps, tanning parlors or tanning pills.
• Pay extra special attention to changes in skin moles during adolescence, pregnancy and menopause when hormonal changes take place in the body.
Although the scientific evidence is not fully developed, there is enough to suggest that women at high risk should discuss the use of oral contraceptives, estrogens, and even the question of whether or not to get pregnant, with their specialists. The most important point to remember is that for persons at high risk, careful, regular self examination, combined with regular visits to a physician who specializes in melanoma will detect skin changes early when they can be carefully cared for.
How can I do a skin exam for melanoma?
The American Cancer Society suggests the following skin exam monthly, after a bath or a shower:1. Use a full length mirror and a hand mirror so you can check any moles, blemishes or birthmarks from the top of your head to your toes, noting anything new a change in size, shape or color or a sore that does not heal.
2. Examine your body front and back in the mirror, then right and left sides, arms raised.
3. Bend elbows and look carefully at forearms and upper underarms and palms.
4. Sit, if that is more comfortable, to look at backs of the legs, feet and spaces between toes and soles.
5. Examine the back of your neck and scalp with the help of a hand mirror, part your hair (or use blow dryer) to lift it and give you a closer look at the scalp.
6. What you are looking for is something different and doing the exam regularly will help you to know what is normal for you and make you feel confident. If you find something, check with your doctor.
Where does malignant melanoma metastasize?
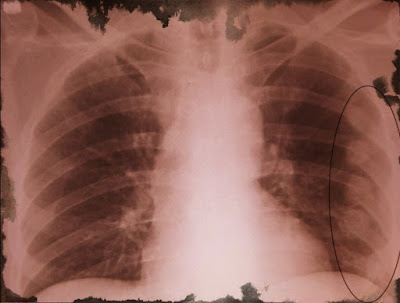
Malignant melanoma can metastasize to any part ofthe body but most commonly to the lungs, liver, and brain. The cells in malignant melanoma show a tendency to metastasize early, traveling through the lymph system and/or the blood system. The commonest route of spread is to the regional lymph nodes.What kind of doctor treats melanomas?
Melanomas are usually found by dermatologists, who usually perform the biopsy, which is then read by a pathologist. If the lesion is found to be malignant, further treatment should be carried out by a specialist either a surgeon who specializes in cancer or a medical oncologist.Is there more than one kind of malignant melanoma?
There are four fairly distinct forms of primary melanoma. They are superficial spreading melanoma, nodular melanoma, acral lentiginous melanoma, and lentigo maligna melanoma. Superficial spreading melanoma and nodular melanoma start from a preexisting mole or as a new growth. Acral lentiginous melanoma appears as a dark mark on the palms, soles, or around the nails. Lentigo maligna melanoma (also known as Hutchinson's melanotic freckle) is a relatively rare tissue abnormality which tends to occur on the face or in areas of the body exposed to the sun in light skinned individuals.What will the doctor do to a mole which has shown some change?
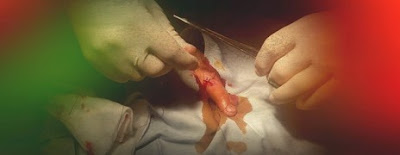
The doctor will arrange to have it removed for examination under the microscope. If it is small, he will take out the whole mole. If it is large, a partial biopsy will be done. It is generally considered wise for the doctor to take out the entire mole if possible, although there is no strong scientific evidence that a partial biopsy is harmful to the patient.Is it easy for the pathologist to tell whether or not the mole is malignant melanoma?
Diagnosis of this kind calls for an experienced pathologist, since malignant melanoma is a very difficult cancer to diagnose correctly. If there is any doubt at all about the diagnosis, the slides should be reviewed by several pathologists before any decision about treatment is made.After biopsy, what other tests are needed before treating malignant melanoma?
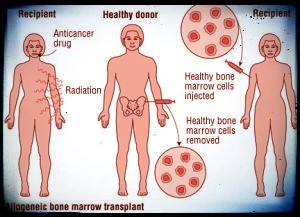
Usually, before any treatment is begun, patients with malignant melanoma undergo a complete evaluation. This usually includes a complete physical, documentation ofthe size and location of any tumor present and the site of primary origin, a history of past and current symptoms, complete blood count, a survey of blood chemistry, and a chest xray. In addition, if needed, a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy, x-rays of the skull and lumbar spine, liver and spleen scans, an electroencephalogram and brain scan, and a stool examination for the presence of occult blood are done.What is the treatment for malignant melanoma?
The treatment for malignant melanoma depends upon the location, extent, and stage of the disease. If the microscopic examination shows that the mole is a malignant melanoma, then further surgery is usually done. The doctor will remove some of the normal appearing skin around the mole. Sometimes the nearby lymph glands are also removed.Is chemotherapy ever used for malignant melanoma?
Sometimes single drug or combination chemotherapy is used, usually in combination with surgery or immunotherapy. If a limited treatment of a single part or organ of the body is needed, chemotherapy in isolation perfusion (introducing the drug to an isolated part of the circulatory system) may be the treatment.Is radiation treatment ever used for malignant melanoma?
Although surgery is generally considered the treatment of choice for malignant melanoma, radiation therapy is sometimes used for treatment, especially for those patients who cannot have an operation for some reason. Radiotherapy is used in certain eye tumors and is frequently used to control localized pain.What is the role of immunotherapy in malignant melanoma?
There is a great amount of research now going on in the use of immunotherapy as an adjuvant therapy for malignant melanoma. Clinical trials are being conducted with immunostimulants such as BCG and monoclonal antibodies.How are monoclonal antibodies used in treating melanoma?
In some centers, monoclonal antibodies are being used to see if the melanoma has spread anywhere else in the body. This is done by attaching radioactive material to monoclonal antibodies and, with x-rays, determining if the antibody shows up in any other part of the body.There are also investigational treatments using monoclonal antibodies. In some centers, toxins are attached to the antibody with the substance given intravenously to the patients. Some patients with certain stages of melanoma are also being treated with interferon. Other treatments under discussion include using antibodies combined with interferon and the use of tumor necrosis factor, a natural substance which selectively kills tumor cells.
Will reconstructive surgery be needed in a person with malignant melanoma?
It depends upon the location and the extent of the operation. Patients with facial and neck areas involved usually need cosmetic surgery, either skin grafts or other plastic surgery.Other articles
What is intraocular melanoma?
IS MALIGNANT TUMOR DANGEROUS?
Signs and Symptoms of Skin Cancer



Comments
Post a Comment